Reorganization: the Watch becomes the center of the hut (February 1943-September 1944)
Introduction
The search services for cribs and their use via menus merge to form the "Watch". Members of its staff manage one or more keys.
The Enigma evolves (appearance of the reflector D) as well as the procedures, which complicates the work of the personnel of Hut 6.
After some time, the Hut 6 organization no longer held in building Hut 6. In February 1943, Hut 6 and all its annexes were brought together in a new building: Block D.
From May 1943, a contingent of Americans will complete the British BP teams as well in Hut 3, Hut 4, Hut 6, Hut 8. An American team (The US 6812th Signal Security detachment) will manage a dozen bombes.
In autumn 1943, Milner-Barry took over as head of Hut 6, Welchman having been appointed the Assistant Director of Mechanization at BP.
It was also during the fall of 1943 (September 1) that the military and air force abandoned the use of the kenngruppe to discriminate against Enigma networks. This was a big blow for Hut 6 and resulted in a significant slowdown in the processing of messages in terms of their recording. The RR section needed to be expanded.
From the end of 1943, Hut 6 was able to share the 4 rotor bombes of the Op20g present in the USA which were designed primarily against the Enigma of the navy.
The war
On the Eastern Front, the major event was the surrender of the German 6th Army at Stalingrad in February 1943. It was a turning point in the war. Overall, the Russians are taking back the lost territories. In July 1943 it was the famous tank battle of Kursk which defeated the Germans who no longer had the initiative on the Russian front.
From June 1943, the allies began a strategic bombing campaign against Germany to lower the morale of the population.
In North Africa, the German and Italian armies were caught in pincers and finally surrendered in May 1943. From July 1943, it was the Italian campaign: the allies land in Sicily and then went up to Italy.
But of course the great event of this period is the opening of a new front with the Allied landings in Normandy from June 1944. Gradually France is liberated.
Keys
The number of keys is increasing further: ninety keys are managed daily by Hut 6, this corresponds to 3000 messages per day.
Organization
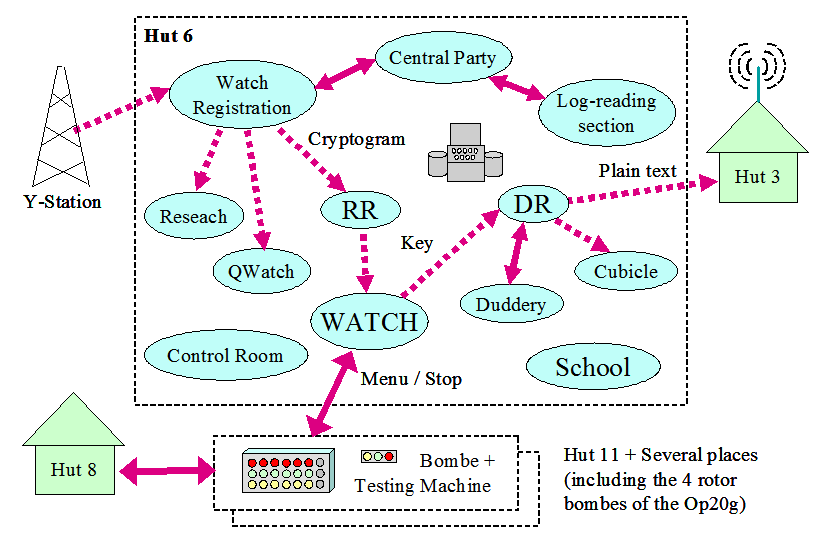
The main change during this period is the creation of the "Watch" which becomes the center of the hut. The search services for cribs (CR1) and their use via menus (MR1) merge to form the “Watch”. Members of its staff manage one or more keys.
Similarly, sections CR2 and MR2 will reform the “Research” section.
The Qwatch section (Quiet-Watch and pronounced quatsch) deals with keys that are not broken on a regular basis. It is also called the "fourth watch" because it does not work in three shifts but at normal times.
The traffic intercepted by the Y services is sent by teleprinter to Hut 6. The messages received are processed by the watch registration section. The messages corresponding to networks which are regularly broken are processed in priority and are sent to the RR service. The others are sent either to the Research section or to the Qwatch section.
The RR (Registration Room) service takes care of sorting the messages according to their network (key) according to kenngruppe and other information (radio frequency, etc.). The preambles are recorded on a Blist (Banister List). The messages are then sent to the Watch.
It is the Watch which has the role of breaking the operational keys thanks to the bombes. When a key has been broken, it is transmitted to the DR section which is responsible for decrypting the messages thanks to the Typex which emulates the Enigma.
Many messages cannot be decrypted because there were transmission errors in the body of the message or in its header. In this case, the Duddery section is trying to decipher them. This section belongs to bombe control room which is itself part of Hut 11 (the bombes which are in BP).
Then the messages are transmitted to Hut 3, but before they are analyzed by the Cubicle section which indexes them (search for new cribs,…).
The central party analyzes the logs kept by the radio operators to reconstruct the radio networks every day from the frequencies and call signs used but also from the chats and the direction finding (D / F).
The log-reading subsection of the central party searches for re-encoding, routine cribs, cillies, and cryptographically relevant information from chats between radio operators. This subsection being the largest in terms of number of people (ninety-five staff in May 1943).
There are of course the Control Room section as well as the school.
The means (bombes)
- 1943 June 72 (58 standard three-rotors bombs + 18 Jumbos)
- 1943 December 87
- 1944 December 152
Staff
In autumn 1943 Hut 6 had grown to over 450 staff.
To serve the bombes: 900 Wrens and 75 RAF mechanics to maintenance them.